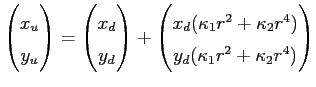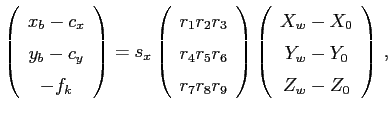Next: Stereo Geometry
Up: Stereo Vision
Previous: Camera Model with Lens
Camera Calibration
Basic camera calibration is the recovery of the effective focal length ![]() and the principle
and the principle
point ![]() in the image plane or, equivalently, recovery of the position
in the image plane or, equivalently, recovery of the position
of the center of projection
![]() in the image coordinate system. This is
in the image coordinate system. This is
referred to as interior orientation in photogrammetry. Additionally, customary cameras have appreciable geometric distortions, but only nonlinear camera calibration techniques take them into account. If the distortion is modelled, it can be distinguished between distorted
![]() and undistorted
and undistorted
![]() image coordinates. The relation is given by
image coordinates. The relation is given by
| (2.12) |
The relationship between the target coordinate system and the camera coordinate system is referred to as exterior orientation. The relation between the image- and the world-coordinate system can be written as
where
 image coordinate of the projected point
image coordinate of the projected point

 coordinate of the intersection between the optical axis and the image plane
coordinate of the intersection between the optical axis and the image plane scale factor against the spatial sampling frequency
scale factor against the spatial sampling frequency distance between the center of the lens and the image plane
distance between the center of the lens and the image plane coefficients of the rotation matrix
coefficients of the rotation matrix

 world coordinates of the projected point
world coordinates of the projected point
 coordinates of the center of projection in world coordinates
coordinates of the center of projection in world coordinates
To find a solution for Equation 2.13 we have to find corresponding image and world coordinates. Often this work is done by the calibration technique and need not be done by hand.
So far many calibration techniques have been published. According to [MK97], they can be
categorized into four major techniques:
- Techniques involving full scale nonlinear
optimization - [Tsa86,Fai75,Sob73]. The accuracy obtained by these methods is very high. But it is very time consuming due to the nonlinear optimization used.
- Perspective transformation matrix using linear equation
- [DH73,AAK71]
The benefit of these techniques is their linearity. The computation is fast, unfortunately lens distortion cannot be modelled because it is not linear (Equation 2.11). By solving an overdetermined system of linear equations the perspective camera matrix can be computed. The DLT (Direct Linear Transformation) is one example for this technique.
- Two plane method
- [MBK71,IPS85] Only linear equations have to be solved, but the relation between the world and the camera coordinate system is assumed to be known.
- Geometric techniques
- [FB86,LT88] Only linear equations have to be solved to get the outer orientation of the camera, but neither the focal length nor the distortion coefficients can be computed.
Normally, camera parameters have only to be calculated once, thus a nonlinear optimization techniques can be used. However, sometimes the parameters have to be calculated several times during operation, in this case a linear technique should be preferred. The two plane method makes only sense, when the relation between the world and the camera coordinate system is known and does not change during operation. In general, the decision which calibration technique to choose depends on time and accuracy constraints.
Next: Stereo Geometry
Up: Stereo Vision